Not like Home windows and macOS, putting in Linux is not really easy. Looking Linux on the web will deliver you so many working methods with completely different names, none of them explicitly known as “Linux.” Why is that this so?
Linux is more and more turning into the working system of selection for seasoned tech geeks and informal customers alike. However why are there 1000’s of working methods or “distributions” all known as “Linux”? And why do builders hold creating extra working methods of the identical sort? Let’s discover out.
What Are Linux Distributions?
First, it is very important know what Linux really is. Linux is not an working system however somewhat a kernel, the adhesive that connects your laptop’s {hardware} with the working system. If you launch an app in your laptop by clicking on an icon, it is the kernel that communicates with the working system to launch the app and show the output on the display screen utilizing the {hardware}, i.e., the monitor.
An working system consists of an underlying kernel, purposes, and sometimes a graphical consumer interface. Linux is the kernel, and all working methods that use it are known as “Linux distributions.” The time period “distribution” comes from the method of sharing Linux-based OSes with different customers, often known as “distributing” because the kernel and the OS are typically free.
What Spawned So Many Linux Distros?
The Linux kernel is licensed underneath the GNU Basic Public License, which provides anybody permission to view, edit, and distribute any purposes of the kernel. But it surely wasn’t at all times like this.
Earlier, Unix was a preferred working system, however its supply code was owned by AT&T. After a while, BSD (Berkeley Software program Distribution), an working system closely primarily based on Unix, originated on the College of California, Berkeley. There have been different working methods primarily based on Unix on the time as effectively, and all of them had been very completely different from one another.
The unavailability of a regular for making a Unix-based OS and the resistance between the OSes on the time gave start to an period often known as the “Unix wars.” Totally different distributors distributing their variations of Unix began organising their very own requirements, together with AT&T and BSD.
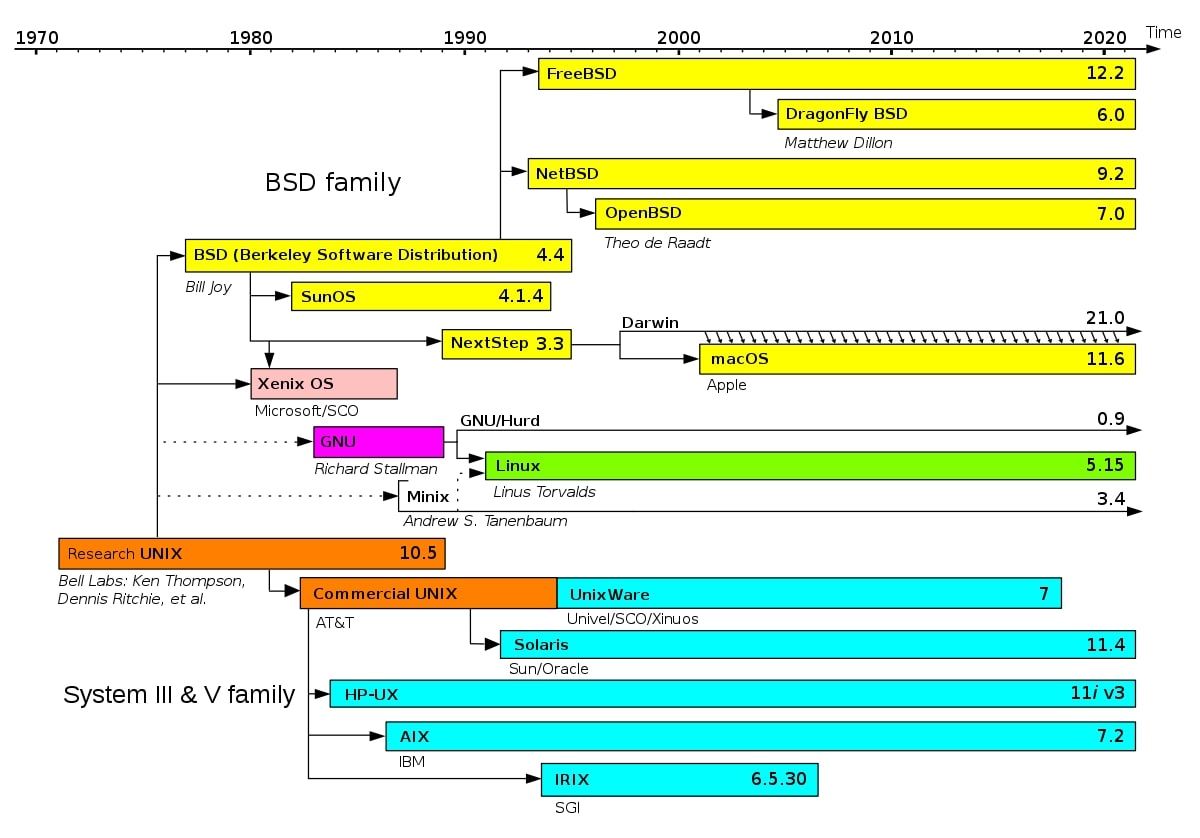
In 1983, Richard Stallman began the GNU Venture, specializing in the event and distribution of free and open-source software program. The GNU Venture aimed to create a free model of Unix, a model that anybody might replicate and distribute freely.
Many apps had been developed underneath GNU’s Basic Public License on the time, together with TAR and Emacs. However the challenge lacked an open-source kernel, the a part of a pc that helps the OS and the apps work together with the {hardware}.
In 1991, eight years after the GNU Venture began, Linus Torvalds began creating Linux. And a yr later, Linux was re-released underneath the Basic Public License, turning into what we now know as GNU/Linux. Because the Linux kernel was licensed underneath GPL, anybody might create an working system on prime of the kernel and distribute it freely.
The power to spin up your personal working system free of charge inspired many builders to begin their distribution. A number of distros together with Debian, Crimson Hat, and Slackware had been launched on the time, kickstarting the Linux revolution.
Why Are New Linux Distributions Created?
The primary cause why builders hold creating and distributing new Linux-based OSes is that they merely can. The Linux kernel is free. The apps are free. The sources to create an entire working system on prime of the kernel are free.
These days, folks not often create a distro from scratch. As an alternative, they take one other in style distro and both construct a brand new OS utilizing the previous one as a base or reskin it with a brand new graphical consumer interface and added purposes.
Ubuntu has a number of reskins of itself, specifically Xubuntu, Kubuntu, and Lubuntu. The one distinction between these three flavors is the desktop surroundings. As an alternative of the default custom-made GNOME desktop that comes preinstalled on Ubuntu, Xubuntu, Kubuntu, and Lubuntu ship with XFCE, KDE Plasma, and LXDE, respectively.
The first purpose of an working system is to make desktop computing simpler for customers. When somebody desires a brand new characteristic in an working system, the normal path to go for is offering suggestions to the corporate that develops the OS. The GNU Venture has utterly modified this movement.

It is the customers who use, develop, present suggestions, implement suggestions, and in the long run, distribute an open-source distro. You are free to create your personal distro and add the options you need within the OS of your desires.
Anybody with an identical ideology and opinions can contribute to the challenge and begin serving to the builders. There is no must contact an organization or fill out a suggestions kind simply to get an additional characteristic added to the OS.
Not solely customers, however even large corporations create new in-house distributions for intracompany utilization. Microsoft’s CBL-Mariner is a well-liked instance. That is primarily as a result of large corporations do not wish to use distros created by different customers and would somewhat develop their very own working system both from scratch or on prime of one other mainstream distro.
The Linux challenge has grown to an extent the place tech giants like Google have began relying on the Linux kernel for a few of their tasks. Take Android and Chrome OS for instance. Android makes use of the Linux kernel underneath the hood and Chrome OS is constructed on prime of Gentoo Linux, a distro launched in 2000.
One more reason for desktop Linux’s fragmentation is the quite a few varieties of units obtainable. Other than desktop computer systems, different units like those primarily based on ARM processors, additionally want an working system to run. Linux solves this by offering a base to the builders to create an OS for any processor household they need.
Raspbian OS is a distro created particularly for Raspberry Pi units. You may also discover numerous distros developed to run on older processors which can be left unsupported by proprietary OS distributors.
Do We Actually Want So Many Distributions?
For those who’re somebody who merely wants a pc and an working system to get issues executed, in fact not. You may get away with utilizing any working system so long as it suits your payments. However for many who wish to be spoilt for selections in relation to their units and digital life, Linux is the one to go for.
You’ll be able to both attempt a few Linux OSes and settle with the one you discover the most effective or hold distro-hopping and testing new distros. Linux offers you that selection. So long as folks hold supporting and contributing to the open-source ecosystem, you may hold seeing new distros being developed and launched free of charge on the web.
That’s How Open-Supply Works!
Despite the fact that many proprietary OSes like Android and macOS have a closed-source codebase, they’ve used Linux as a basis for his or her tasks. It’s utterly acceptable because the license the Linux kernel is launched underneath permits anybody to change and distribute the code with no restrictions.
Because of the huge group help behind Linux-based working methods, new and unique options are repeatedly added to the distros. Though you could find many such options on different proprietary OSes like Home windows and macOS, a few of them are restricted to solely a handful of Linux distributions.
Learn Subsequent
About The Writer