Linux has an abundance of software program, however whenever you first make the swap, chances are you’ll be pissed off by the dearth of names you are conversant in. Should you’ve used Linux for some time, you may additionally develop disillusioned by what can really feel like a comparatively sluggish price of change or the enduring lack of sure sorts of software program.
Why are sure apps but to return to Linux, and what’s holding again the group from producing extra alternate options? Let’s discover out.
1. There Are So Many Variations of Linux
Whenever you develop software program for Home windows, you solely want to check your software program on a handful of methods: the newest model of Home windows, the earlier one, and perhaps, relying on whether or not your program is focusing on very slow-moving companies, the model earlier than that. It is comparatively simple.
On Linux, there’s a sea of various variations, referred to as distributions. Even if you happen to restrict your self to probably the most distinguished ones, that would nonetheless imply supporting half a dozen distros.
For example you determine to assist solely Ubuntu, the preferred model on private computer systems. With Ubuntu’s launch schedule that means an improve each six months, even that may be extra work than it sounds.
Common package deal codecs have improved the scenario, however there are nonetheless a number of choices. Should you’re focusing on Ubuntu, it is smart to go along with the Snap format, however most different distros have extra of an affinity for Flatpak as a substitute. A number of have settled on AppImage.
In idea, apps in any of those three codecs can run on any distro. However for instance your distro ships an older model of the background parts Flatpaks must run. Meaning an app might lack the performance that the developer expects you to have. The scenario is enhancing, however Linux nonetheless has methods to go to make the panorama simpler for app builders.
2. Linux Has an Unclear Funding Mannequin
Linux is as a lot a philosophy as it’s an working system. Technically Linux is not even an working system, however a kernel, the side of your pc that allows the buttons you press to really do one thing and your display to point out what’s being finished.
The desktop interfaces and the apps that we use have actually nothing to do with Linux. You’ll be able to run a lot of the identical software program on FreeBSD, which does not use the Linux kernel—and you’ll’t run most of those packages on Chromebooks or Android, which do.
The philosophy underpinning desktop Linux is the idea of software program freedom, that code must be seen and freely shared. That is the one identified manner to make sure that packages aren’t doing one thing shady and to really give folks possession over their units.
A results of that is that it is tough to cost instantly for software program. You’ll be able to promote a program beneath a free software program license, however because the code is freely out there, there may be nothing to cease another person from compiling and distributing one other copy of your program that does not value cash.
As such, folks growing Linux and associated software program have needed to experiment with other ways of funding their work. Many are volunteers who fund their work with a special full-time job. Many volunteers are college students. Some folks land jobs the place they’re paid to develop one side of Linux, however of their free time, they contribute to a different. Only some builders are in a position to usher in sufficient donations to compensate for his or her efforts.
There is not a transparent funding mannequin for somebody seeking to make a dwelling creating apps for Linux like they will for different platforms except these apps are proprietary, a sort of software program many Linux customers need nothing to do with.
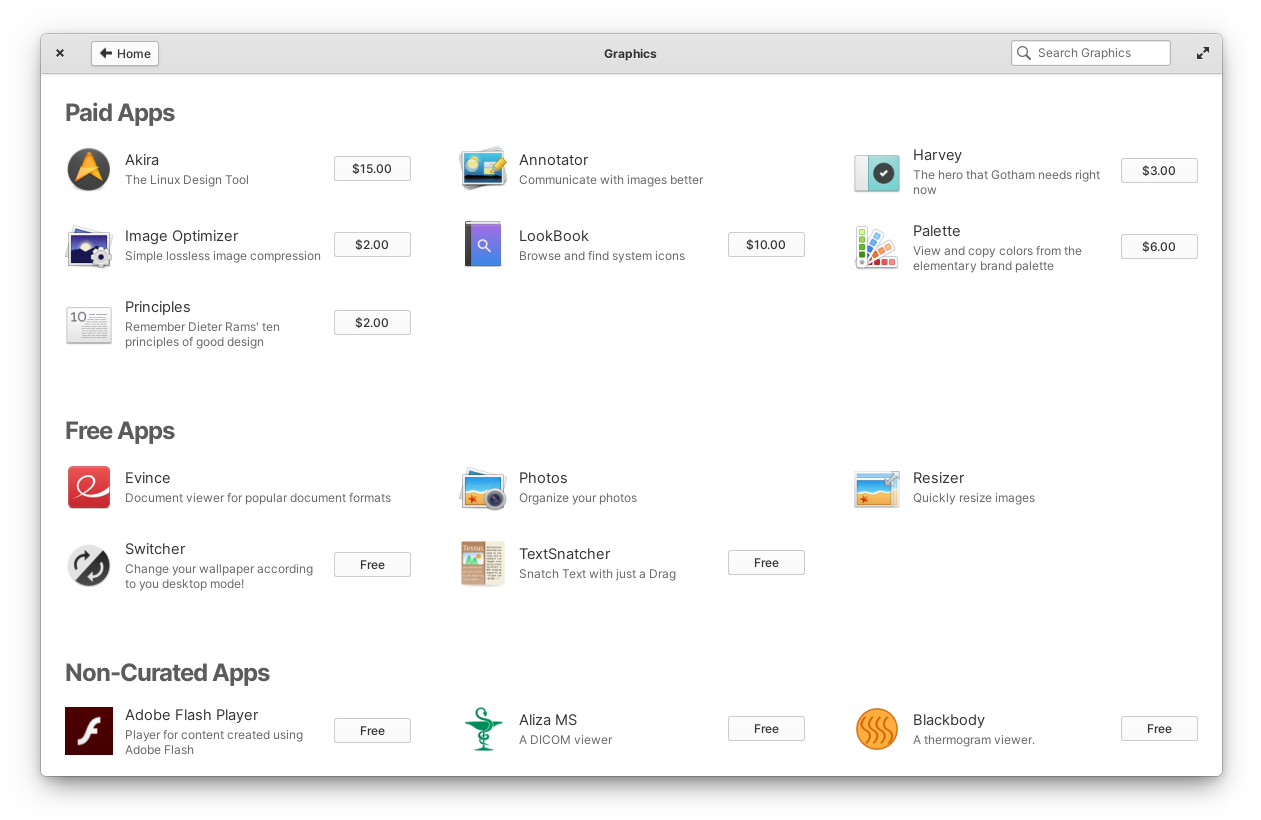
One Linux distro, elementary OS has a pay-what-you-can strategy for the free and open-source apps launched in AppCenter (pictured above), however to this point folks haven’t paid sufficient for app builders to contemplate this a full-time job.
3. There Is a Lack of Cash to Go Round
This unclear funding mannequin is a part of the explanation many Linux communities haven’t got entry to sufficient cash to do the type of work they want to do. Individuals engaged on a specific desktop atmosphere might need to design a full suite of apps that combine with their interface however lack the assets to pay folks to do the work.
This lack of assets means free software program communities are primarily reliant on volunteers to step up. If there is not a volunteer with the curiosity, the time, and the ability set, then usually occasions the specified software program does not get made.
This additionally leads volunteers to cooperate on sure packages. This is not essentially a nasty factor. However if you happen to’re questioning why there aren’t extra open supply alternate options to LibreOffice, that is partially as a result of it usually makes extra sense to volunteers, and even corporations using a handful of builders, to contribute the performance they need to LibreOffice than to make one other suite from scratch.
4. Open Dialogue Comes With Disagreements
With volunteers doing a lot of the event on Linux, and with each the open-source philosophy and monetary constraints pushing folks to work collectively, quite a lot of communication is critical for all of the items to return collectively.
Since folks usually cannot appeal to paid builders, they must persuade folks to volunteer their time for moral or sensible causes. This implies weblog posts or in-person speeches that may have the impact of inspiring some and laying aside others.
Open supply growth additionally tends to occur out within the open, over mailing lists and the likes of GitHub and GitLab. These conversations usually contain variations of opinion. Rifts can type, main builders to go develop their very own interface from scratch, duplicating work that another person has already finished.
That is a part of the explanation Linux has so many interfaces that technically do the identical factor, simply in numerous methods.
All of that is earlier than the individuals who use all of this software program get entangled. Customers can have passions which can be even stronger than the builders, particularly once they really feel powerless {that a} beloved program is altering its look or a characteristic they depend on goes away solely. Some builders face a lot hostility that they stop free software program growth attributable to burnout.
5. The Linux Desktop Has Low Market Share
After all, it is not solely software program developed particularly for Linux that folks need. Many need entry to the identical software program they use on Home windows and macOS, equivalent to Photoshop. A few of these packages do make their solution to Linux, equivalent to Steam, however many don’t.
Linux’s comparatively small market share is an enormous cause why. Whereas Linux is dominant on servers and supercomputers, solely a comparatively small proportion of individuals use Linux on their private computer systems. This nonetheless interprets to hundreds of thousands of individuals, however many corporations decide it is simply not price the price of paying builders to take care of assist for a 3rd working system once they’re making sufficient cash already.
6. Companies Have Copyleft Licensing Issues
Some corporations have reservations in regards to the copyleft licensing that the majority software program on Linux makes use of. These organizations might need to develop software program or combine sure parts, however they worry ending up legally required to open supply all of the code of their proprietary program consequently.
Many corporations have an aversion to the GNU Public License, which requires any software program which makes use of code shared beneath the GPL to be made open supply.
Firms that do make the most of free software program usually favor code out there beneath permissive licenses, like MIT and Apache, that let folks to make use of the code with no requirement that the ensuing program turn out to be free and open supply itself.
For an organization whose enterprise mannequin revolves across the sale of closed supply code, misreading a free software program license and opening themselves as much as authorized litigation could be a risk to the corporate’s backside line.
Nonetheless, Linux App Growth Goes On!
Regardless of these challenges, Linux continues to draw software program builders. The free and open nature of Linux makes it an excellent place for a pupil to study. Open code additionally makes it attainable for folks to make use of present apps as the muse for brand spanking new ones, somewhat than ranging from scratch.
Then there are individuals who agree with Linux values, who cannot deliver themselves to finally assist Microsoft, Apple, or Google make more cash. This retains the ecosystem vibrant and lively, even when you need to be keen to check out apps whose names you have by no means heard earlier than.
Learn Subsequent
About The Creator